Kubernetes Session Two
Recap of Kubernetes Resource Object I
- What is a Pod?
- Minimal unit for Kubermetes
- How to create a Pod?
kubectl run db --image mongo- Declarative way to create Pod
cat pod/db.yml
- Run multiple containers in a Pod
cat pod/go-demo-2.yml
- Monitor Pod health
cat pod/go-demo-2-health.yml
- Use ReplicaSet to scale Pod
cat rs/go-demo-2.yml
Kubernetes Resource Object II
Service
Service is an abstraction that defines a set of Pods and a policy to access them.
Service Types
- Cluster IP
- Expose the service on a cluster-internal IP
- NodePort
- Expose the service on each Node’s IP at a static port
- <NodeIP>: <NodePort>
- LoadBalancer
- Expose the service externally using a cloud provider’s load balancer
- ExternalName
- Map the service to an external address(e.g. kubernetes.io)
Expose the service
Use
kubectl exposeto expose a resource as a new Kubernetes Service. That resource can be a Deployment, another Service, a ReplicaSet, a ReplicationController, or a Pod.
Define a new ReplicaSet:
cat svc/go-demo-2-rs.yml
Different with rs/go-demo-2.yml:
- name: db
image: mongo:3.3
command: ["mongod"]
args: ["--rest", "--httpinterface"]
ports:
- containerPort: 28017
protocol: TCP
Create ReplicaSet object and get state from Kubernetes:
kubectl create -f svc/go-demo-2-rs.yml
kubectl get -f svc/go-demo-2-rs.yml
Expose the ReplicaSet as a new Service:
kubectl expose rs go-demo-2 --name=go-demo-2-svc --target-port=28017 --type=NodePort
Describe the service:
kubectl describe svc go-demo-2-svc
Service labels are inherited from Pods and selector matches the one from the RepicaSet.
PORT=$(kubectl get svc go-demo-2-svc -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}")
IP=$(minikube ip)
open "http://$IP:$PORT"
open "http://localhost:$PORT"
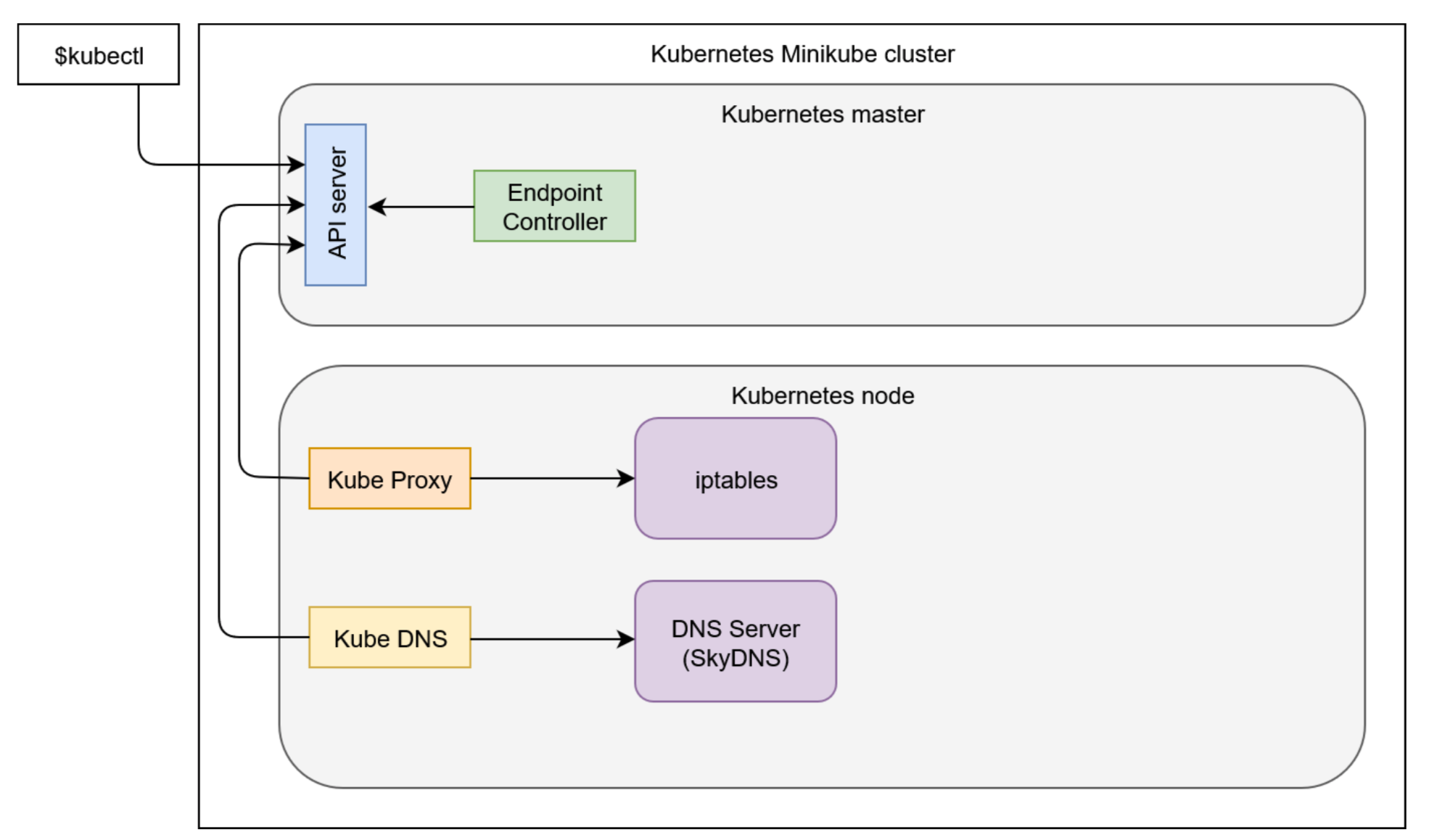
Process involved of above command:
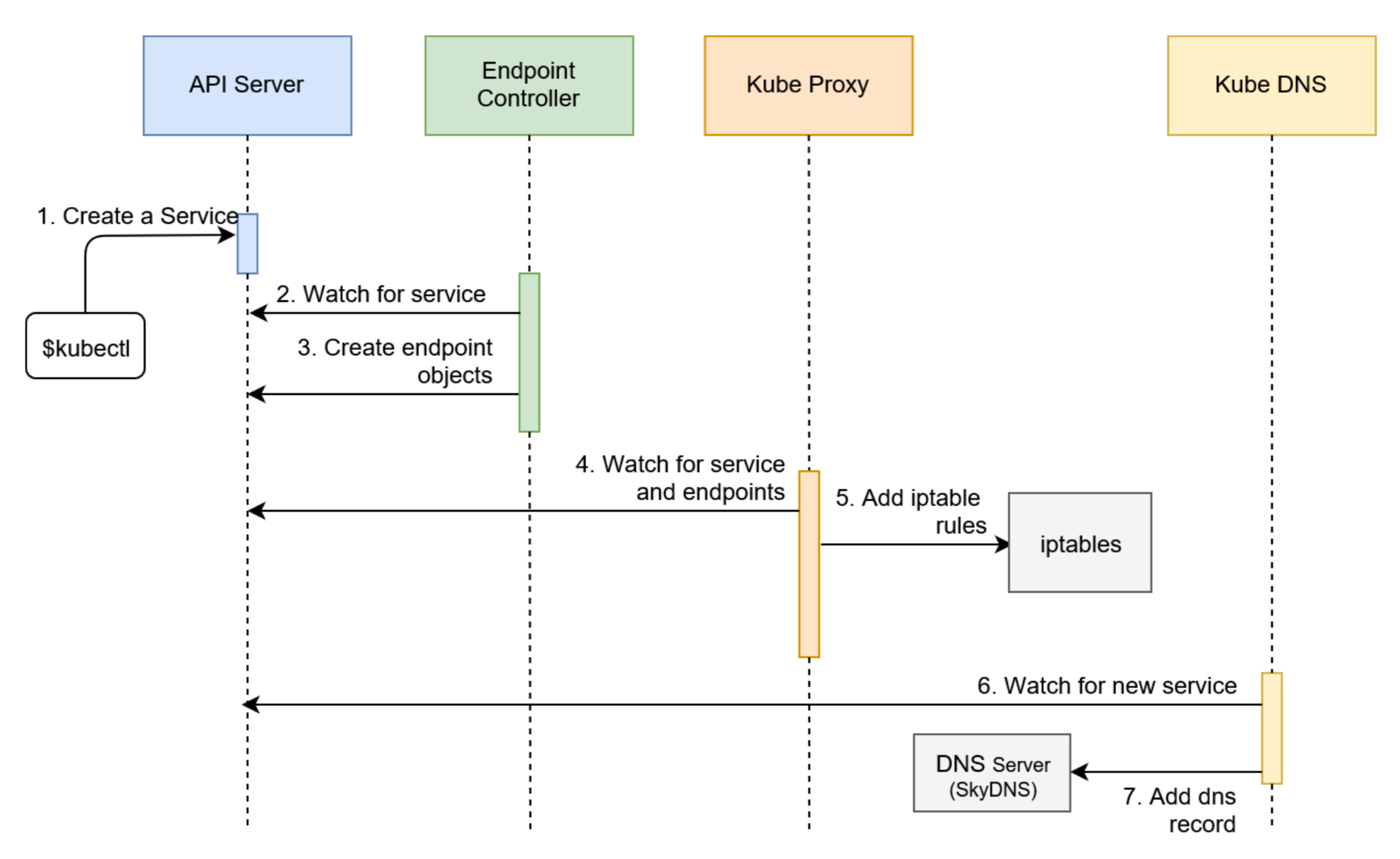
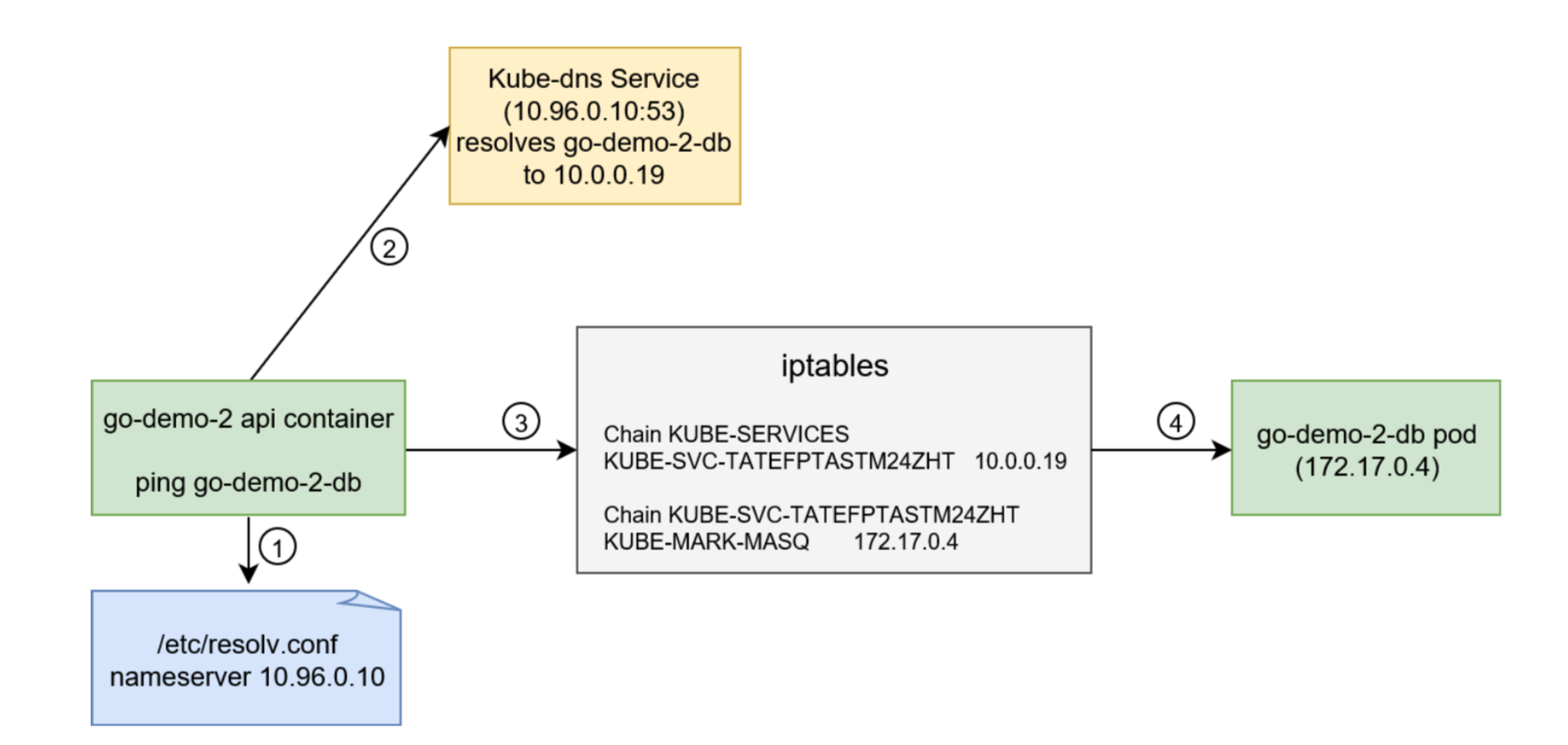
Note: Kube-proxy added iptables rules which capture traffic to the Service port and redirect it to endpoints. For each endpoint object, it adds iptables rule which selects a Pod.
Delete the service:
kubectl delete svc go-demo-2-svc
Declarative way to create service
cat svc/go-demo-2-svc.yml
Create and get status of the service:
kubectl create -f svc/go-demo-2-svc.yml
kubectl get -f svc/go-demo-2-svc.yml
Access the service:
open "http://$IP:30012"
open "http://localhost:30012"
Get endpoint status and list the pods that should receive the requests:
kubectl get ep go-demo-2 -o yaml
Destroy the ReplicaSet and Service:
kubectl delete -f svc/go-demo-2-svc.yml
kubectl delete -f svc/go-demo-2-rs.yml
####Services can also abstract other kinds of backends
- You want to have an external database cluster in production, but in test you use your own databases.
- You want to point your service to a service in another
Namespaceor on another cluster. - You are migrating your workload to Kubernetes and some of your backends run outside of Kubernetes.
Define a Service without a selector:
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: my-service
spec:
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 9376
Because this service has no selector, the corresponding Endpoints object will not be created. You can manually map the service to your own specific endpoints:
kind: Endpoints
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: my-service
subsets:
- addresses:
- ip: 1.2.3.4
ports:
- port: 9376
Accessing a Service without a selector works the same as if it had a selector. The traffic will be routed to endpoints defined by the user (1.2.3.4:9376 in this example).
###Split pods and establish communication via services
Best Practice: A Pod contains only one container.
Create db ReplicaSet:
cat svc/go-demo-2-db-rs.yml
kubectl create -f svc/go-demo-2-db-rs.yml
Create db Service:
cat svc/go-demo-2-db-svc.yml
kubectl create -f svc/go-demo-2-db-svc.yml
Create api ReplicaSet:
cat svc/go-demo-2-api-rs.yml
kubectl create -f svc/go-demo-2-api-rs.yml
Create api Service:
cat svc/go-demo-2-api-svc.yml
kubectl create -f svc/go-demo-2-api-svc.yml
List all the objects created:
kubectl get all
Visit the service:
PORT=$(kubectl get svc go-demo-2-api -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}")
curl -i "http://$IP:$PORT/demo/hello"
curl -i "http://localhost:$PORT/demo/hello"
Delete all the objects:
kubectl delete -f svc/go-demo-2-db-rs.yml
kubectl delete -f svc/go-demo-2-db-svc.yml
kubectl delete -f svc/go-demo-2-api-rs.yml
kubectl delete -f svc/go-demo-2-api-svc.yml
Define mutiple objects in one YAML file
cat svc/go-demo-2.yml
Create objects:
kubectl create -f svc/go-demo-2.yml
kubectl get -f svc/go-demo-2.yml
Visit the service:
PORT=$(kubectl get svc go-demo-2-api \
-o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}")
curl -i "http://$IP:$PORT/demo/hello"
Discover Services
Services can be dicovered in two modes:
- Environemtn variables
- DNS
A look at environment variables in one of the Pods:
POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pod \
--no-headers \
-o=custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name \
-l type=api,service=go-demo-2 \
| tail -1)
kubectl exec $POD_NAME env
Describe the service:
kubectl describe svc go-demo-2-db
Process involved:
Deployment
ReplicaSet is used to scale Pod. But ReplicaSet are rarely used independently. Instead use Deployment to create ReplicaSet.
A Deployment controller provides declarative updates for Pods and ReplicaSets.
cat nginx-deployment.yaml
Create a deployment:
kubectl create -f nginx-deployment.yaml --record
Scale the deployment:
kubectl scale deployment nginx-deployment --replicas 10
Update image:
kubectl set image deployment/nginx-deployment nginx=nginx:1.9.1
Check update history:
kubectl rollout history deployment/nginx-deployment
Roll back:
kubectl rollout undo deployment/nginx-deployment
Summary
Kubernetes Cluster Overview
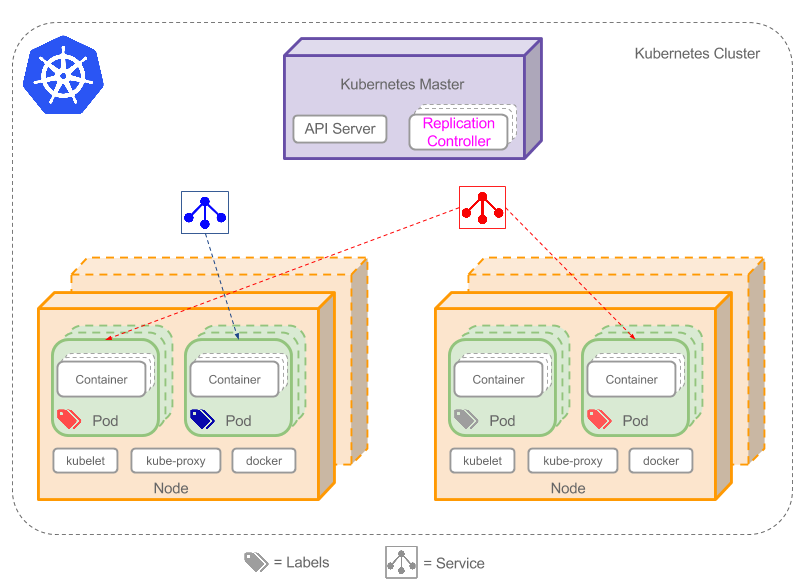
Involved Kubernetes Objects
| Category | Object Name |
|---|---|
| Resource & Configuration | Pod, ReplicaSet, ReplicationController, Deployment, StatefulSet, DaemonSet, Job, CronJob |
| Storage | Secret, ConfigMap, LocalVolume, PersistentVolume |
| Network | Namespace, Service, Ingress |
- Pod
- ReplicaSet(ReplicationController)
- Service
- Deployment
| Application Type | Resource Object |
|---|---|
| Long-running | Deployment |
| Batch | Job/CronJob |
| Node-daemon | DaemonSet |
| Stateful Application | StatefulSet |